We suggest in this section to familiarize yourself with brief information about what this or that method of treatment means. This section will be updated.
Splinting
This is an effective way to save teeth, even with advanced forms of periodontitis. This is a method of restoring and strengthening the dentition. It is carried out by installing a tire connecting the movable teeth into a single block. Helps to avoid their loss, to prevent the risk of gum disease. It is used for advanced periodontitis, when tooth mobility is observed (salvation of badly shattered teeth).
Indications for splinting teeth:
- Abandoned periodontitis
- Mobility and displacement of the dentition
- Exposure of tooth roots
- Severe bleeding and inflammation of the gums
- The appearance of pronounced gingival pockets
- Bite deformity associated with a change in the location of the teeth
- Post-traumatic syndrome caused by a fracture of the jaw
Types of splinting
A broad classification is used for this procedure. The duration of splinting can be:
- Temporary – up to 3 months. Used to reduce the burden on soft tissues during treatment
- Long-term – up to 1 year. Used in individual cases
- Permanent – protects teeth from falling out for a long time
Permanent splinting can be:
- removable
- non-removable
The first is relevant in cases where the patient has partial loss of teeth. A non-removable splint is applied to relieve pressure on the periodontal tissue.
Clasp splinting
Clasp splinting is performed using a metal splint. It is more traumatic and noticeable, but there are cases when this is the only possible option. For example, with fractures of the jaw of varying complexity.
How is teeth splinting performed?
The procedure algorithm depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and the chosen technique. But conditionally, the procedure is carried out in several stages:
- Local anesthetic injection
- Creation of a longitudinal groove in the posterior walls of the teeth
- Installing splinting material into it
- Tire masking with filling material
Did you know?
For a long time, metal remained the only material for splinting teeth. Today, more progressive solutions are used: fiberglass, aramid thread.
Aramid thread
Aramid thread is also considered a progressive method of splinting. It preserves the integrity of the teeth and reduces their mobility, as well as protects against horizontal stress.
Fiberglass tires
Fiberglass teeth splints differ significantly from metal ones:
- Minimally injure the tooth
- Are able to preserve even those teeth that are very loose
- Optimally distributes the chewing load
- Provide convenient hygiene procedures
- Aesthetic and discreet
What threatens the wrong bite?
- If the bite is incorrect, there is a risk of not only the development of tooth pathologies, but also disorders of the internal organs of a person. Today, few people still know about the dangers of such a condition for general health, and therefore are not in a hurry to the orthodontist.
- It can lead to a violation of the functions of the digestive tract, brain, and even the posture of a person. The consequences, if the bite is incorrect, can manifest as persistent headaches. In this case, it is enough to fix the problem to get rid of the accompanying symptoms and prevent the development of complications in the future.
- With an incorrect bite, the head of the maxillary joint is displaced and puts pressure on the area in which the nerves and blood vessels are concentrated. There may also be a spasm of facial muscles.
What is the danger of malocclusion for the circulation of the head?
Many people have no idea how dangerous a bad bite is for the bloodstream and how the two systems are connected. It is important to note that the upper jaw stops growing at age 14, while the lower jaw completes its formation only by 19-21 years.
Improper occlusion: consequences for dental health
First of all, the consequences of malocclusion will be present on the part of the teeth. In patients with this problem, there is an uneven distribution of the load on the teeth and periodontal tissues, which leads to consequences.
If there is a malocclusion, the consequences may also be the appearance of early signs of aging. This is due to the wear of the teeth, their displacement, which leads to wrinkles, sagging lips and cheeks.
If the patient has a malocclusion, the consequences can be as follows:
- recession of the gums – exposure of the root of the tooth due to excessive stress on certain areas of the periodontium
- caries – in violation of the bite is often difficult to clean some teeth, which leads to accumulation of plaque, bacteria and subsequent destruction of the crown
- periodontitis – is accompanied by excessive mobility of teeth and the exposure of their roots, is observed in almost all patients after 30-40 years in the absence of timely treatment
- dysfunction of the temporomandibular joint due to increased load on it – as a result, there is a click, pain in the masticatory muscles, inflammation may develop
The harm of a malocclusion to the work of the gastrointestinal tract
The gastrointestinal tract is also subject to increased stress if the malocclusion is not corrected in time. Due to the uneven load on the chewing apparatus, food is not properly crushed and enters the stomach in chunks. This leads to its longer digestion, fermentation, impaired absorption of nutrients, which in turn is very harmful to the general health of a person.
What to do and how to correct an incorrect bite?
Faced with a similar problem, patients often ask the question: how to correct a malocclusion and restore the normal position of the dentition? Only a qualified orthodontist can answer it after performing an examination.
Knowing how an incorrect bite affects a person, you should carefully monitor the condition of the dentoalveolar apparatus and promptly eliminate the appearance of anomalies.


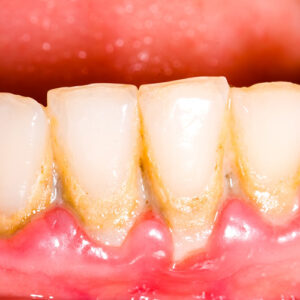 Dental calculus
Dental calculus Do you know what you can or cannot eat in braces?
Do you know what you can or cannot eat in braces? About oral hygiene
About oral hygiene Are records suitable for adults?
Are records suitable for adults?